Articles In Press
"Articles In Press"是经过同行评审并被接受发表的文章。在正式发表之前还可能有内容修改,但可以使用DOI对文章进行引用。正式发表后,该文章将不再在此处展示,现有链接将自动重定向到文章的最终版本。
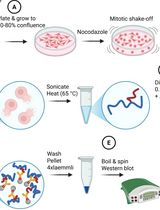
Denaturing SUMO Immunoprecipitation From Mitotic Cells
Small ubiquitin-related modifiers (SUMOs) are covalently conjugated onto the proteome and serve as signaling molecules in many aspects of eukaryotic cell biology, from S. cerevisiae and C. elegans to H. sapiens. The conjugatable SUMO variants, SUMO1 and the almost identical SUMO2 and SUMO3 (designated SUMO2/3), are processed by an E1(SAE1:SAE2)-E2(UBC9)-E3 enzyme cascade to produce SUMO-modified proteins. The prerogative of the SUMO biology field is to identify and study the specific proteins undergoing SUMOylation, which grants us insights into the biological pathway of interest. This protocol was developed using the human osteosarcoma cell line U2OS to enable the investigation of SUMO conjugates in mitosis, the cell division phase of the cell cycle. We enrich the cell population for mitotic cells, which are isolated and subjected to stringent lysis conditions involving a high concentration of SDS and DTT in RIPA buffer, to promote complete protein denaturation. The lysates in high SDS RIPA buffer are diluted to reduce the overall SDS concentration and undergo conventional immunoprecipitation using SUMO1- or SUMO2/3-specific antibodies bound to protein A/G agarose beads. The samples are then compatible with downstream readouts such as western blots and mass spectrometry. This protocol detects endogenous SUMOylated proteins and avoids exogenous SUMO overexpression, which can alter SUMO conjugate formation. Furthermore, this denaturing protocol ensures only SUMOylated proteins are immunoprecipitated, and not their interactors.
A Simple Method for Estimating the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Phenoloxidase Proteins in Insect Tissues
Laccase2 (Lac2), a member of the phenoloxidase (PO) family, is an essential oxidase for melanin pigmentation in insects. The identification of the in vivo spatial distribution of Lac2 is crucial for understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying color pattern formation. However, it is technically difficult to determine the distribution because Lac2 expression peaks at late pupal stages, when adult cuticle sclerotization has already begun. Here, we report a simple and rapid protocol for estimating the distribution of endogenous PO proteins, prophenoloxidases (proPOs) and phenoloxidases (POs), in insect tissues. In this method, the spatial distribution of endogenous PO proteins is estimated based on staining patterns formed by dopamine melanin synthesis in tissues incubated in a solution containing isopropanol and dopamine. We validated that tissues collected at approximately 80% of the total pupal duration yielded staining patterns corresponding to adult melanin-forming regions in three insect species. By comparing staining patterns across developmental stages, this protocol enables estimation of the timing of color pattern formation. Furthermore, the contrast between stained and unstained regions within the same tissue allows region-specific sampling, thereby facilitating an investigation of the underlying molecular mechanisms regulating spatial PO distribution. Taken together, this method facilitates the study of melanin biosynthesis and enables the identification of the genes involved in regulating color pattern formation. This protocol does not require antibodies, transgenic lines, or specialized equipment and can be completed within a short time frame. Its effectiveness has been validated in multiple coleopteran and lepidopteran species, demonstrating its broad applicability as a versatile tool for studying insect pigmentation and color pattern formation.
MDISCO: A High-Throughput Tissue-Clearing Protocol for Preservation of Endogenous Fluorescence in Whole Mouse Brains
Organic solvent–based tissue clearing methods are widely used for whole-brain imaging but often compromise endogenous fluorescence. Existing protocols, such as iDISCO and fluorescence-preserving variants, have improved optical transparency but still present trade-offs between fluorescence retention, tissue stability, and workflow complexity. Here, we present MDISCO, a modified iDISCO-based clearing protocol designed to enhance preservation of endogenous fluorescence while maintaining high transparency and stable tissue morphology. MDISCO is directly compared with FDISCO+, an established fluorescence-preserving protocol, for the preservation of endogenous tdTomato and YFP. Performance across clearing steps is evaluated by measuring brain weight, anteroposterior and mediolateral dimensions, and optical transparency before and after solvent clearing and refractive index matching. Fluorescence preservation is assessed using whole-brain light-sheet microscopy with standardized imaging parameters to enable direct comparison. This protocol provides an accessible and high-throughput, reproducible workflow for solvent-based clearing with robust endogenous fluorescence preservation, offering clear advantages for whole-brain 3D imaging of genetically encoded fluorescent reporters.
Isolation, Culture, and Differentiation of Bovine Muscle Resident Stem Cells
Bovine muscle satellite cells (MuSC) and fibro-adipogenic progenitor cells (FAP) are muscle resident stem cells that are responsible for postnatal muscle growth, intramuscular fat deposition, and extracellular matrix generation. These cells are of increasing interest for the cultivated meat community due to their ability to generate all the major components of meat; additionally, these cells are of interest to conventional animal science research to elucidate mechanisms to improve meat quality. To use these cells for these goals, efficient and accurate cell isolation, culture, and differentiation are essential to evaluate their cell fate decisions and behaviors. In this protocol, we detail a simultaneous isolation of both MuSCs and FAPs with multiple intermediate stopping points, allowing for flexibility for day-of time constraints. We also detail improved growth conditions to maximize cell expansion and procedures to assess cell differentiation. This protocol provides a flexible isolation procedure that is compatible with sampling in modern slaughterhouses or from biopsies. Additionally, the differentiation procedures provide improved differentiation but still allow in vitro treatment and assessment.
3D STED Super-Resolution Imaging Strategy for Visualizing Synaptic Nano-architecture in Brain Cryosections
Super-resolution imaging of synapses in intact brain tissue remains challenging because light scattering, photobleaching, and limited probe penetration, along with antigen accessibility within the densely packed postsynaptic densities (PSDs), constrain resolution and labeling efficiency. Here, we present a protocol utilizing thin brain cryosections and tau-stimulated emission depletion (STED) nanoscopy to visualize the intricate nano-architecture of excitatory synapses in situ. Slicing the brain into 6 μm sections allows for highly efficient and even penetration of probes throughout sections while ensuring that the resolution is not significantly impacted by the imaging depth of the tissue. We outline step-by-step instructions for labeling pre- and postsynaptic nano-architecture using antibodies and nanobodies, highlighting how fixative choice influences the labeling efficiency of synaptic proteins. While this protocol is compatible with both confocal and super-resolution imaging, when combined with rapid image acquisition times of tau-STED, it enables clear separation of key synaptic features in three dimensions with minimal photobleaching. Thus, this approach enables robust multiplex imaging of fluorescently labeled synaptic proteins in the brain, providing exceptional spatial resolution for visualization and quantification of synaptic nanoarchitecture in its native environment.
A Novel Sequencing Method for Quantification of ZIKV RNA in Individual Cells
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) is a powerful technique for exploring cellular heterogeneity and host–pathogen interactions. This protocol details the Zika virus (ZIKV)-targeted scRNA-seq workflow for preparing high-quality single-cell suspensions from the whole brain tissues of neonatal mice, high-quality single-cell sorting, cDNA reverse transcription, amplification, ZIKV enrichment and host transcriptome library preparation, and sequencing dataset integration in downstream analysis to complete the quantification of ZIKV RNA in individual cells.
Mag-Net Strong Anion Exchange Enables Isolation of Ovarian Cancer Ascites Extracellular Vesicles for Proteomic Biomarker Discovery
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanoscale particles secreted by all cells and present in all biological fluids, where they carry molecular cargo reflective of health and disease states. Their diagnostic potential is often obscured by the high abundance of non-EV proteins and lipoproteins (e.g., albumin, apolipoproteins) that complicate proteomic analysis of primary biofluids, such as ascites fluid. Conventional isolation strategies face a persistent trade-off between EV purity and yield. To overcome this, a magnetic bead-based protocol (Mag-Net) to enrich EVs according to electrochemical surface charge using strong anion-exchange chemistry (SAX) was adapted for proteomics. Our workflow is specifically adapted to ascites fluid from human or murine sources. This approach effectively separates EVs from high-abundance proteins and lipoproteins, enabling proteomic profiling from as little as 2 μL of ascites fluid. Demonstrated in both murine and human ovarian cancer models, Mag-Net offers a reproducible, scalable, and automation-ready solution for EV isolation from various biofluids.
Tandem RNA and Protein Extraction: A Platform for Maximizing the Use of Limited Ex Vivo Tissue Samples
Human tissue samples represent the gold standard for obtaining clinically relevant and translatable insight into disease processes that in vitro systems cannot fully reproduce. However, patient-derived samples are often limited in size and availability, limiting the number of downstream assays that can be performed. To maximize the use of invaluable human samples, we present a protocol for the tandem extraction of high-quality RNA and protein from the same tissue section. This method has been optimized for 15–30 mg tissue sections, enabling more experimental conditions and technical replicates, while minimizing intrasample variability associated with heterogeneous tissues. This protocol also avoids potentially hazardous solvents present in phenol-chloroform-based methods such as TRIzol, providing a safer and more accessible workflow without compromising biomolecule integrity. This protocol was developed and validated using atherosclerotic plaque tissue from carotid endarterectomy, a very challenging tissue type to work with due to extensive calcification, necrosis, and limited surgical availability. We have also validated this method using mouse aortic tissue and cultured THP-1 cells, demonstrating its versatility across sample input types. As this protocol relies on standard column-based RNA extraction kits and commonly available reagents for protein precipitation and extraction, this methodology is widely accessible and easy to implement as a standard, streamlined workflow.
Controlled Transmission of a Fijivirus Under Field Conditions Using Mass-Reared Planthoppers
Mal de Río Cuarto disease, caused by a Fijivirus, is a major constraint for maize production in Argentina. The traditional evaluation of resistant hybrids is limited by the low efficiency of natural virus transmission and the lack of standardized field inoculation methods. We developed a protocol that combines laboratory mass-rearing of the planthopper vector Delphacodes kuscheli with a controlled field transmission system. The method involves the synchronized production of large insect populations, acquisition of viruliferous vectors under controlled conditions, and their safe transport to the field using specialized containers. Transmission is achieved through individual cages placed on maize seedlings, ensuring high inoculation pressure under field-like conditions. This protocol enables reliable and reproducible virus transmission, facilitating large-scale screening of maize hybrids and other cereals. Its main advantages are the high throughput of vector production, improved transmission efficiency, and adaptability to diverse experimental designs.
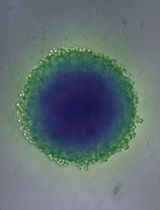
A Simple and Cost-Effective Method for Generating Spheroids From Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line (MDA-MB-231)
Breast cancer (BC) is the most frequently diagnosed malignancy in women and a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Current clinical management relies on molecular classification—based on estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), HER2, and Ki67 expression—to guide prognosis and therapy. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), which lacks ER, PR, and HER2 expression, represents 15%–20% of cases and is characterized by aggressive behavior, early recurrence, and a paucity of targeted treatment options. These challenges underscore the urgent need for improved preclinical models that better recapitulate tumor biology to accelerate therapeutic discovery. While conventional monolayer (2D) cultures have contributed significantly to cancer research, they fail to mimic critical features of the three-dimensional (3D) tumor microenvironment (TME), thereby limiting clinical translation. To address this gap, 3D spheroid models have emerged as a powerful intermediary, more accurately replicating in vivo conditions such as cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions, nutrient and oxygen gradients, and the development of hypoxic cores. These features make spheroids a physiologically relevant platform for studying complex processes like metastasis, drug resistance, and treatment response. Here, we present a robust, simple, and cost-effective protocol for generating uniform 3D spheroids. Our method enables consistent monitoring of spheroid formation and growth over time, with quantitative, image-based size analysis to ensure reproducibility and scalability. Designed for flexibility, the protocol is broadly applicable across diverse cell types, effectively bridging the gap between traditional 2D cultures and complex in vivo studies. By providing an accessible and reliable model of the 3D TME, this protocol opens new avenues for high-throughput drug screening, mechanistic studies of tumor progression, and the advancement of personalized medicine strategies in breast cancer and beyond.
Microinjection of Synthetic Peptides Into Caenorhabditis elegans
The genome of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans encodes at least 160 predicted peptide precursor genes that can generate over 300 bioactive peptides, the functions of most of which remain unknown. Phenotypes resulting from deletion or transgenic expression of peptide genes are readily assayed, but genetic dissection of individual peptide activities is often confounded when a single gene encodes multiple peptides or when distinct peptides act redundantly. Here, we describe a protocol for direct microinjection of chemically synthesized peptides into individual worms. This approach permits investigation of the effects of an individual peptide while providing precise temporal control over peptide delivery.
Radial Profile-Based Quantification of Centrosomal Proteins
Centrosomes are dynamic organelles critical for mitotic spindle assembly and cilia formation. Here, I describe a protocol for quantifying relative centrosomal protein abundance in Drosophila melanogaster embryos using radial profile analysis of fluorescence intensity. The method involves embryo collection, manual dechorionation, mounting for live imaging, confocal microscopy, and subsequent image analysis. Radial profiling allows quantification of relative protein abundance together with its spatial distribution at the centrosome, providing either relative or normalized intensity profiles. I then outline how this approach can be integrated with complementary techniques such as fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) and super-resolution imaging, in this case, three-dimensional structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM). Combining radial fluorescence profiling with these imaging modalities enables high-resolution, quantitative analysis of dynamic centrosome assembly in a genetically tractable system.
A Cytosine Deaminase–Based Genomic Footprinting Assay (cFOOT-seq) for Detecting Transcription Factor Occupancy
Transcription factors (TFs) regulate gene expression by binding to cis-regulatory elements in the genome. Understanding transcriptional regulation requires genome-wide characterization of TF occupancy across different chromatin contexts, yet simultaneous assessment of TF binding for multiple factors remains technically challenging. Here, we describe a detailed and reproducible protocol for cFOOT-seq, a cytosine deaminase–based genomic footprinting assay by sequencing, which enables antibody-independent, base-resolution profiling of chromatin accessibility, nucleosome organization, and TF occupancy. In cFOOT-seq, the double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) cytosine deaminase SsdAtox converts cytosine to uracil in accessible chromatin, whereas TF binding and nucleosome occupancy locally protect DNA from deamination. Using the FootTrack analysis framework, deamination patterns generated by cFOOT-seq are quantitatively analyzed to derive standardized footprint and chromatin organization profiles at base resolution across the genome. Because cFOOT-seq preserves genomic DNA integrity during deamination-based footprinting, it is compatible with ATAC-seq-based chromatin enrichment. ATAC-combined implementations reduce sequencing depth requirements and improve scalability for footprint-focused analyses, supporting applications in low-input and single-cell settings. This protocol provides a practical framework for genome-wide TF footprint profiling and can be readily applied to dissect gene regulatory mechanisms in development, immunity, and disease, including cancer.
A Bioinformatics Workflow to Identify eccDNA Using ECCFP From Long-Read Nanopore Sequencing Data
Extrachromosomal circular DNA (eccDNA) is a type of circular DNA that exists independently of chromosomes and has garnered significant attention in various fields, particularly in the context of smaller eccDNAs, which have considerable roles in gene regulation through various mechanisms. Current methods such as Circle-Seq and 3SEP can enrich small eccDNAs during sample preparation, but most bioinformatics pipelines remain challenging, exhibiting low accuracy and efficiency. This protocol describes the detailed workflow of a newly developed bioinformatics analysis pipeline, named EccDNA Caller based on Consecutive Full Pass (ECCFP), to accurately identify eccDNA from long-read Nanopore sequencing data. Compared to other pipelines, ECCFP significantly improves detection sensitivity, accuracy, and runtime efficiency. The process includes raw data quality control, trimming of adapters and barcodes, alignment to a reference genome, and identification of eccDNA, with detailed results encompassing accurate positioning of eccDNA, consensus sequences, and variants of individual eccDNA.
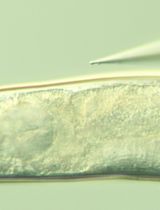
A Rapid and Visual Soybean Hairy Root Transformation Protocol Using the RUBY Reporter
Agrobacterium rhizogenes–mediated hairy root transformation provides a rapid platform for gene function analysis prior to stable whole-plant transformation. However, most existing hairy root transformation methods rely on tissue culture and require chemical or fluorescence-based selection, which increases experimental complexity. Here, we describe a tissue culture–free soybean hairy root transformation protocol incorporating the RUBY visual reporter system. While this work does not introduce a new transformation concept, it presents a streamlined implementation of established soybean hairy root methodologies that emphasizes procedural simplicity, reduced handling, and faster access to functional root material. Transgenic roots expressing RUBY can be directly identified by red pigmentation with the naked eye. In RUBY-positive roots, candidate genes driven by the CaMV 35S promoter showed higher expression levels than those in empty-vector controls, indicating that the system supports effective gene expression. Using this procedure, clearly identifiable transgenic hairy roots can be obtained within 20 days. Overall, this protocol simplifies induction and screening while reducing operational complexity and equipment requirements.
A Guide to Reproducible Cellulose Synthase Density and Speed Measurements in Arabidopsis thaliana
Cellulose synthase complexes (CSCs) play a central role in plant cell wall formation. Their dynamic behavior at the plasma membrane leads to the deposition of cellulose microfibrils into the apoplastic space, thereby shaping the architecture and mechanical properties of the cell wall. Although previous imaging studies have provided important insights into CSC dynamics and localization, standardized and reproducible workflows for quantitative measurements of CSC speed and density remain limited. Here, we present a reproducible live-cell imaging and analysis workflow for quantifying the speed and density of fluorescently labeled CSCs at the plasma membrane in Arabidopsis thaliana. The protocol integrates optimized spinning-disk confocal imaging, surface-based projection of z-stack recordings, automated detection of diffraction-limited CSCs foci, and kymograph-based speed measurements using freely available tools in Fiji. While selected steps, such as region of interest definition and parameter selection for spot detection or trajectory analysis, remain user-guided, these decisions are constrained to well-defined stages within an otherwise standardized pipeline, thereby reducing variability and improving reproducibility across experiments. The workflow has been validated across multiple tissues, reporter lines, genetic backgrounds, and perturbation conditions in Arabidopsis and enables robust comparative analysis of CSC dynamics. Beyond CSCs, this workflow is expected to be adaptable to other fluorescently labeled proteins that appear as diffraction-limited foci at or near the plasma membrane.
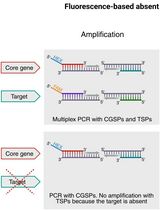
Fluorescence-Based Absent Allele-Specific Amplification (FAASA) for High-Throughput Detection of Absent Alleles
In wheat and other crops, some genes display presence/absence variation, and it is occasionally beneficial to select for the absent allele to remove a functional gene. However, current high-throughput genotyping methods used to detect the absence of genes tend to be inconsistent and inconclusive. Kompetitive allele-specific PCR (KASP) and PCR allele competitive extension (PACE) are two well-established methods for allele-specific polymerase chain reaction (AS-PCR) assays, each using fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) to generate a signal for each allele, typically targeting biallelic single-nucleotide polymorphisms. KASP and PACE methods are more difficult to apply to alleles with presence/absence variation because the lack of amplification of the absent allele is indistinguishable from a failed PCR. Here, we present a multiplex fluorescence-based absent allele–specific amplification (FAASA) method using the PACE marker system (compatible with KASP markers) to detect the absence of one particular or all alleles of a target sequence using a primer mix consisting of one target-specific primer pair (TSP) and a second primer set specific to a highly conserved endogenous gene known as a core gene–specific primer pair (CGSP). The forward primer of each pair is tagged with a 5′ terminal tail complementary to dye-labeled oligonucleotides in commercially available FRET cassettes. Lines that amplify only the core gene do not carry the target, while lines that amplify both the core gene and the target carry alleles of both the core gene and the target. The inclusion of the CGSPs allows researchers to confidently distinguish lines with absent alleles of the target from lines with failed PCR reactions, which can happen due to various reasons, including inadequate DNA quality or quantity.
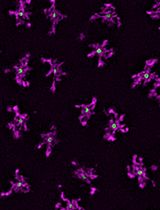
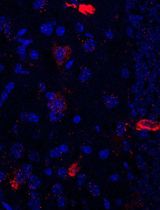
Simultaneous Immunofluorescence-Based In Situ mRNA Expression and Protein Detection in Bone Marrow Biopsy Samples
Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) can be employed to study the expression and subcellular localization of nucleic acids by using labeled antisense strands that hybridize with the target RNA or DNA molecules. Likewise, immunofluorescence antibody staining (IF) takes advantage of the specific interaction between a fluorophore-labeled antibody and its corresponding antigen. This protocol reports the combination of RNA-FISH and IF antibody staining for simultaneous detection of both RNA transcripts and proteins of interest in routine formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) bone marrow biopsy samples. Herein, we provide a detailed description of the methodology that we have developed and optimized to study the spatial expression of two transcripts—TGFB1 and PDGFA1—in human hematopoietic (CD45+) and non-hematopoietic (CD271+) cells in the bone marrow of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
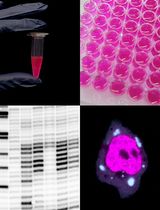
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA) for Assessing RNA–Protein Binding and Complex Formation Using Recombinant RNA-Binding Proteins and In Vitro–Transcribed RNA
Evaluating RNA–protein interactions is key to understanding post-transcriptional gene regulation. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSAs) remain a widely used technique to study these interactions, revealing information about binding affinities and binding modalities, including cooperativity and complex formation. Here, we detail, in a step-by-step protocol, how to perform EMSAs. We describe how to generate, purify, and quantitate 32P-radiolabeled RNA by in vitro transcription, as well as the expression and purification of recombinant RNA-binding proteins in E. coli using ELAV as an example. We then describe how to set up binding reactions using serial dilutions in a microtiter plate format of recombinant ELAV and in vitro–transcribed RNA and how to perform EMSAs using native low-crosslinked acrylamide gels, with detailed graphically supported instructions and troubleshooting guides.
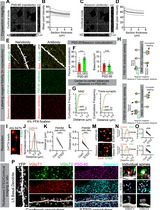
Using combined fluorescent in situ hybridization with Immunohistochemistry to co-localize mRNA in diverse neuronal cell types
Understanding gene expression within defined neuronal populations is essential for dissecting the cellular and molecular diversity of the brain. mRNA assays provide a direct readout of gene expression, capturing transcriptional changes that may precede or occur independently of protein abundance, whereas protein assays reflect the cumulative effects of translation, modification, and degradation. Moreover, in histological analysis, immunohistochemical protein detection results in visually diffuse labeling, which makes it difficult to quantitatively assess levels and locations of expression at high resolution. Here, we present a protocol that allows for mRNA detection in single neuronal cell types with a high degree of sensitivity and anatomical resolution. This protocol combines fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) with immunohistochemistry (IHC) on the same tissue section. Briefly, FISH is carried out by ACDBio RNAscope® fluorescent in situ hybridization technology, which involves processing the tissue sections, followed by signal amplification. This involves target retrieval, probe hybridization, and signal enhancement. Then, the tissue section is processed for IHC, which involves blocking nonspecific sites and incubation with primary antibodies, followed by development of a fluorescent signal with secondary antibodies. Typically, visual mRNA detection with FISH can be seen as individual puncta, whereas targeting the protein with an antibody results in filled cells or processes. The variation in staining pattern allows for the quantification of distinct mRNA transcripts within different neuronal populations, which renders co-localization analyses easy and efficient.
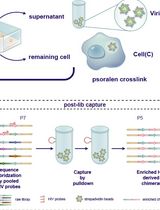
High-resolution mapping of RNA-RNA interactions across the HIV-1 genome with HicapR
基于 HiCapR 的 HIV-1 全基因组 RNA–RNA 相互作用高分辨率图谱构建
The genomes of RNA viruses can fold into dynamic structures that regulate their own infection and immune evasion processes. Proximity ligation methods (e.g., SPLASH) enable genome-wide interaction mapping but lack specificity when dealing with low-abundance targets in complex samples. Here, we describe HiCapR, a protocol integrating in vivo psoralen crosslinking, RNA fragmentation, proximity ligation, and hybridization capture to specifically enrich viral RNA–RNA interactions. Captured libraries are sequenced, and chimeric reads are analyzed via a customized computational pipeline to generate constrained secondary structures. HiCapR generates high-resolution RNA interaction maps for viral genomes. We applied it to resolve the in vivo structure of the complete HIV-1 RNA genome, identifying functional domains, homodimers, and long-range interactions. The protocol's robustness has been previously validated on the SARS-CoV-2 genome. HiCapR combines proximity ligation with targeted enrichment, providing an efficient and specific tool for studying RNA architecture in viruses, with broad applications in virology and antiviral development.
Enhanced RNA-Seq Expression Profiling and Functional Enrichment in Non-model Organisms Using Custom Annotations
Functional enrichment analysis is essential for understanding the biological significance of differentially expressed genes. Commonly used tools such as g:Profiler, DAVID, and GOrilla are effective when applied to well-annotated model organisms. However, for non-model organisms, particularly for bacteria and other microorganisms, curated functional annotations are often scarce. In such cases, researchers often rely on homology-based approaches, using tools like BLAST to transfer annotations from closely related species. Although this strategy can yield some insights, it often introduces annotation errors and overlooks unique species-specific functions. To address this limitation, we present a user-friendly and adaptable method for creating custom annotation R packages using genomic data retrieved from NCBI. These packages can be directly imported as libraries into the R environment and are compatible with the clusterProfiler package, enabling effective gene ontology and pathway enrichment analysis. We demonstrate this approach by constructing an R annotation package for Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, as an example. The annotation package is then utilized to analyze differentially expressed genes from a subset of RNA-seq dataset (GSE292409), which investigates the transcriptional response of M. tuberculosis H37Rv to rifampicin treatment. The chosen dataset includes six samples, with three serving as untreated controls and three exposed to rifampicin for 1 h. Further, enrichment analysis was performed on genes to demonstrate changes in response to the treatment. This workflow provides a reliable and scalable solution for functional enrichment analysis in organisms with limited annotation resources. It also enhances the accuracy and biological relevance of gene expression interpretation in microbial genomics research.
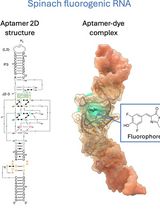
Visualizing diverse RNA functions in living cells with Spinach™ family of fluorogenic aptamers
利用SpinachTM系列荧光适配体可视化活细胞中多种RNA功能
RNA is now recognized as a highly diverse and dynamic class of molecules whose localization, processing, and turnover are central to cell function and disease. Live-cell RNA imaging is therefore essential for linking RNA behavior to mechanism. Existing approaches include quenched hybridization probes that directly target endogenous transcripts but face delivery and sequestration issues, protein-recruitment tags such as MS2/PP7 that add large payloads and can perturb localization or decay, and CRISPR–dCas13 imaging that requires substantial protein cargo and careful control of background and off-target effects. Here, we present a protocol for live-cell RNA imaging using the SpinachTM family of fluorogenic RNA aptamers. The method details the design and cloning of SpinachTM-tagged RNA constructs, selection and handling of cognate small-molecule fluorophores, expression in mammalian cell lines, dye loading, and image acquisition on standard fluorescence microscopes, followed by quantitative analysis of localization and dynamics. We include controls to verify aptamer expression and signal specificity, guidance for multiplexing with related variants (e.g., Broccoli, Corn, Squash, Beetroot), and troubleshooting for dye permeability and signal optimization. Application examples illustrate use in tracking cellular delivery of mRNA therapeutics, monitoring transcription and decay in response to perturbations, and the forming of toxic RNA aggregates. Compared with prior methods, SpinachTM tags are compact, genetically encodable, and fluorogenic, providing high-contrast imaging in both the nucleus and cytoplasm with single-vector simplicity and multiplexing capability. The protocol standardizes key steps to improve robustness and reproducibility across cell types and laboratories.
Enhancement of RNA Imaging Platforms by the Use of Peptide Nucleic Acid-Based Linkers
RNA imaging techniques enable researchers to monitor RNA localization, dynamics, and regulation in live or fixed cells. While the MS2-MCP system—comprising the MS2 RNA hairpin and its binding partner, the MS2 coat protein (MCP)—remains the most widely used approach, it relies on a tag containing multiple fluorescent proteins and has several limitations, including the potential to perturb RNA function due to the tag’s large mass. Alternative methods using small-molecule binding aptamers have been developed to address these challenges. This protocol describes the synthesis and characterization of RNA-targeting probes incorporating a peptide nucleic acid (PNA)-based linker within the cobalamin (Cbl)-based probe of the Riboglow platform. Characterization in vitro involves a fluorescence turn-on assay to determine binding affinity (KD) and selective 2′-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE) footprinting analysis to assess RNA-probe interactions at a single nucleotide resolution. To show the advancement of PNA probes in live cells, we present a detailed approach to perform both stress granule (SG) and U-body assays. By combining sequence-specific hybridization with structure-based recognition, our approach enhances probe affinity and specificity while minimizing disruption to native RNA behavior, offering a robust alternative to protein-based RNA imaging systems.
Amplification-Free Detection of Highly Structured RNA Molecules Using SCas12aV2
The CRISPR/Cas12a system has revolutionized molecular diagnostics; however, conventional Cas12a-based methods for RNA detection typically require transcription and pre-amplification steps. Our group has recently developed a diagnostic technique known as the SCas12a assay, which combines Cas12a with a split crRNA, achieving amplification-free detection of miRNA. However, this method still encounters challenges in accurately quantifying long RNA molecules with complex secondary structures. Here, we report an enhanced version termed SCas12aV2 (split-crRNA Cas12a version 2 system), which enables direct detection of RNA molecules without sequence limitation while demonstrating high specificity in single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) applications. We describe the general procedure for preparing the SCas12a system and its application in detecting RNA targets from clinical samples.